Blogs
Data Visualization: A Key Tool for Effective Decision-Making
Modern data visualization began to develop in the 20th century. It is a technique that comes right after data preparation, aiming to make multiple pieces of information accessible and understandable through visual representations. Data visualization transforms raw data into simple visual graphs that can be read at a glance. Thanks to this practice, data exploration and analysis are facilitated. The data is formatted and colored ergonomically so that the main information stands out immediately. Data visualization highlights complex information, unlike numerical tables or written reports. The visual representations used in data visualization can be varied: graphs, pie charts, diagrams, maps, timelines, infographics, etc.
1. Why is Data Visualization Crucial?
Data visualization plays a fundamental role in information management and decision-making for several reasons:
Clarity and Understanding: Graphical representations of data make information more accessible and easier to understand. Graphs, diagrams, and maps facilitate the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies.
Quick Decision-Making: By visualizing data, decision-makers can quickly grasp essential information and make informed decisions without getting lost in the details.
Effective Communication: Visualizations allow results and analyses to be communicated clearly to stakeholders, facilitating collaboration and engagement.
Problem Detection: Visualization tools help quickly identify problems and opportunities by highlighting gaps between expectations and goals.
2. Best Practices for Data Visualization
Data Visualization Technique 1 – Histogram: A graphical representation of data using bars of different heights, each bar grouping numbers into ranges, also known as a bar chart. A taller bar indicates that more data falls within that range.
Data Visualization Technique 2 – Heatmaps: A unique way of representing data using colors to mark different values. The color difference allows viewers to grasp trends more accurately. Heatmaps are ideal for visualizing correlation matrices and missing values in data.
Data Visualization Technique 3 – Charts: One of the most popular data visualization techniques, with several varieties. We’ve already discussed bar charts and histograms. Other types include line charts, pie charts, scatter plots, and bubble charts.
Data Visualization Technique 4 – Word Cloud: A word cloud is used to indicate the frequency of words used in a set of texts, displayed in a cloud shape. This technique is typically used on unstructured data to show the frequency of a particular word.
Data Visualization Technique 5 – Gauge Charts: Also known as speedometer charts or dial charts, they use needles to display information as if you were reading it on a dial. When using a gauge chart, the value of each needle is read against the colored data range or chart axis.
Data Visualization Technique 6 – Treemaps: These visualize hierarchical data as a set of nested rectangles. Treemaps are another way to visualize the hierarchical structure of a tree diagram while representing the quantities of each category by the area size.
3. Popular Tools for Data Visualization
There are numerous data visualization tools available that can help you create professional graphs and dashboards. Here are some of the most popular:
Tableau: One of the most widely used visualization tools, Tableau allows for the creation of interactive visualizations and dashboards. It offers a wide range of features for data analysis and report generation.
Power BI: Developed by Microsoft, Power BI is a powerful tool for data visualization and report creation. It integrates well with other Microsoft products and offers advanced features for data analysis.
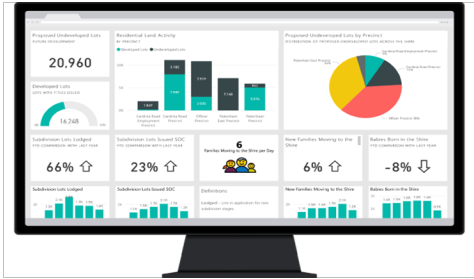
Google Data Studio: A free tool that allows the creation of interactive reports and dashboards using data from Google Analytics, Google Sheets, and other sources.
D3.js: A JavaScript library that allows for the creation of dynamic and interactive data visualizations on the web. D3.js is highly flexible but requires programming skills.
4. Case Studies: Success in Data Visualization
Many companies have used data visualization to achieve impressive results. Here are a few examples:
Netflix: Uses data visualization to analyze user behaviors and recommend personalized movies and series. Graphs help understand subscriber preferences and optimize recommendations.
Uber: Employs visualization tools to analyze driving data and demand trends. Visualizations help optimize routes and improve customer service.
Spotify: Uses data visualization to understand listening habits and recommend playlists and songs tailored to users' tastes.
5. Tips for Effective Data Visualization
To create effective data visualizations, keep these tips in mind:
Know Your Audience: Tailor your visualizations to your target audience. Use appropriate visual elements and levels of detail to meet their specific needs.
Test and Validate: Before finalizing your visualizations, test them with users to ensure they are understandable and useful. Gather feedback and adjust the visualizations accordingly.
Ensure Consistency: Use consistent formats and colors across all your visualizations to facilitate understanding and avoid confusion.
Regular Updates: Ensure that visualizations are updated with the most recent data to maintain their relevance and accuracy.