Blogs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential tools for measuring the effectiveness and success of businesses across various sectors. In the manufacturing industry, KPIs play a crucial role in helping companies track their performance, identify areas for improvement, and achieve their strategic objectives. This article explores the different types of KPIs, their importance, and how to implement them effectively.

1. What is a KPI?
A KPI is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving its key objectives. KPIs can vary significantly depending on the industry and specific goals of the company. They are generally classified into two categories: operational performance KPIs and strategic performance KPIs.
Operational Performance KPIs: These indicators measure the efficiency of daily processes, such as production rate, cycle time, and defect rate.
Strategic Performance KPIs: These indicators are aligned with the company's long-term objectives, including revenue growth, market share, and customer satisfaction.
2. The Importance of KPIs in the Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, KPIs are particularly crucial because they help track and improve production processes. Here are some reasons why KPIs are essential:
Continuous Improvement: KPIs help identify inefficiencies in the production process, enabling continuous improvement.
Informed Decision-Making: The data provided by KPIs allows managers to make decisions based on concrete information rather than assumptions.
Objective Alignment: KPIs ensure that all levels of the organization are working towards common goals.
3. Types of KPIs Used in Manufacturing
There are several KPIs specific to the manufacturing sector. Here are some examples:
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE measures the overall effectiveness of equipment by considering availability, performance, and quality.
Defect Rate: This indicator measures the percentage of defective products compared to the total number of products manufactured.
Production Cycle Time: The total time required to manufacture a product from start to finish.
Capacity Utilization Rate: Measures the percentage of production capacity actually used compared to the total available capacity.
4. How to Implement KPIs
Implementing KPIs requires a structured approach to ensure their effectiveness. Here are some key steps:
Define Clear Objectives: Identify the strategic objectives of the company and align the KPIs with these objectives.
Choose the Right KPIs: Select KPIs that are relevant and measurable. Avoid overwhelming the system with too many indicators.
Data Collection: Establish systems to collect the necessary data accurately and in a timely manner.
Analysis and Interpretation: Analyze the data to understand trends and identify areas needing improvement.
Communication and Action: Share the results with relevant stakeholders and take corrective actions if necessary.
5. Ensuring Successful KPI Implementation with QCDSM and SQCDM
a. Why Use QCDSM
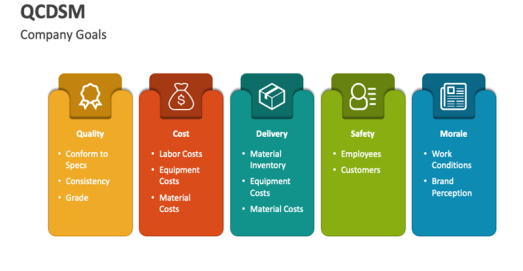
The QCDSM system (Quality, Cost, Delivery, Safety, Morale) is used for several essential reasons:
Overall Performance Improvement: QCDSM allows for a comprehensive evaluation of a company’s performance by integrating key dimensions of production. By monitoring product quality, production costs, delivery times, employee safety, and team morale, companies can identify and address issues at all levels, ensuring continuous improvement.
Resource Optimization: By focusing on cost and delivery, QCDSM helps companies optimize their resources and reduce waste. This not only lowers operational costs but also enhances overall process efficiency.
Enhanced Safety and Morale: By including safety and morale in its performance criteria, QCDSM fosters a safe and motivating work environment. Prioritizing employee safety reduces accidents and work stoppages, while high team morale contributes to better productivity and a positive work atmosphere.
Alignment with Customer Expectations: By monitoring quality and delivery times, QCDSM ensures that products and services meet customer expectations, maintaining high customer satisfaction and strengthening market competitiveness.
b. Why Use SQCDM
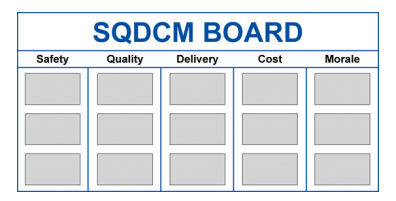
The SQCDM system (Safety, Quality, Cost, Delivery, Morale) is also used for specific reasons:
Safety Prioritization: SQCDM starts with a focus on employee safety. Ensuring a safe work environment minimizes the risk of accidents and occupational illnesses, contributing to a healthy and productive workforce.
Continuous Quality Improvement: SQCDM places quality at the core of its concerns, ensuring that products and services meet high standards. This contributes to customer satisfaction and reduces returns and defects.
Effective Cost and Delivery Management: By focusing on cost and delivery, SQCDM helps companies control expenses and meet delivery deadlines, optimizing production processes and improving profitability.
Employee Engagement and Motivation: SQCDM considers employee morale, fostering a work environment where teams feel valued and engaged. Good morale often translates into better performance and greater efficiency.
6. Concrete Examples of KPI Utilization
To illustrate the importance of KPIs, here are a few concrete examples in the manufacturing industry:
Quality Improvement: One company used the defect rate as a primary KPI to improve product quality. By analyzing the causes of defects, the company implemented corrective measures that reduced the defect rate from 15% to 5% within a year.
Cycle Time Optimization: Another company used production cycle time as a KPI to identify bottlenecks in its manufacturing process. By reorganizing workstations and training employees, the company reduced cycle time by 20%.
7. Challenges in Using KPIs
Although KPIs are powerful tools, their use can present challenges:
Selecting Relevant Indicators: Choosing KPIs that truly reflect the company’s performance can be complex.
Data Collection and Management: Ensuring the accuracy and availability of data may require sophisticated systems.
Result Interpretation: Analyzing data to draw useful conclusions may require advanced analytical skills.
Conclusion
KPIs are indispensable for any manufacturing company aiming to enhance its performance and achieve strategic objectives. By following a structured approach to defining, implementing, and analyzing KPIs, companies can not only identify areas needing improvement but also track their progress towards operational excellence.Sources
Manufacturing.net
A Comprehensive Guide to Manufacturing KPIsForbes
Best Practices for KPIsInsightsoftware
Manufacturing KPIsQCDSM
WHAT IS QCDSM/SQCDM?